Download this schematic diagram.
Datasheet semiconductor component.
1. NE5534
2. MJE350
3. MJE340
4. BD139
5. BC546B
6. BC556B
7. MJE15030
8. MJE15031
9. MJE15003
10. MJE15004
11. BAT85
12. IN4004
13. BY254
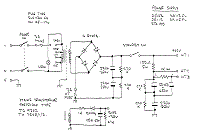
The circuit is being powered by two 15V power supply for each channel, that is regulated by the combination of resistors R7-9 and Zener diodes D1-2. The frequency bandwidth is limited to a specific value due to the presence of low pass filter from R2 & C2 and high pass filter from R3 & C1. The total feedback of the circuit is concentrated on the positive non-inverting input of the IC1 that functions as differential amplifier. The node of R4-5 is applied with the feedback voltage from the output through R6. The current regulated by R10 & R14 across Q1-2 is 10mA as they operate in class A while in class AB, the power transistors Q8-11 operate in the output with a regulated constant current of 100mA each power transistor, done by trimmer TR1 and Q3. This will match the voltage drop at 27mV, higher than the provided voltage of R25-28.
A heatsink with sufficient dimension to provide cooling is placed above Q1-2-3-6-7 to maintain the possible thermic stability while the protection from reverse voltages from the load is performed by diodes D9-10.Additional fan can also be employed to suppress high temperature for efficient operation. The stability during high frequencies is sustained by the Zobel network consisting of R29 & C18. Due to capacitive load, the amplifier output is protected by a 1mm diameter 15-coil inductor L1 with R30 for square pulses passage.
Each power amplifier that is created will correspond to a transformer to handle large capacitors and provide proportional power. The transformer input is connected to the AC line which can incorporate delay circuit for protection from excessive supply. The cables that would carry the current to the amplifier should be appropriate enough.